Summary
Robot on Rails, Red Queen Bio and OpenAI collaborated to develop a robotic system to advance traditionally manual molecular cloning workflows through the integration of artificial intelligence, robotics and computer vision.
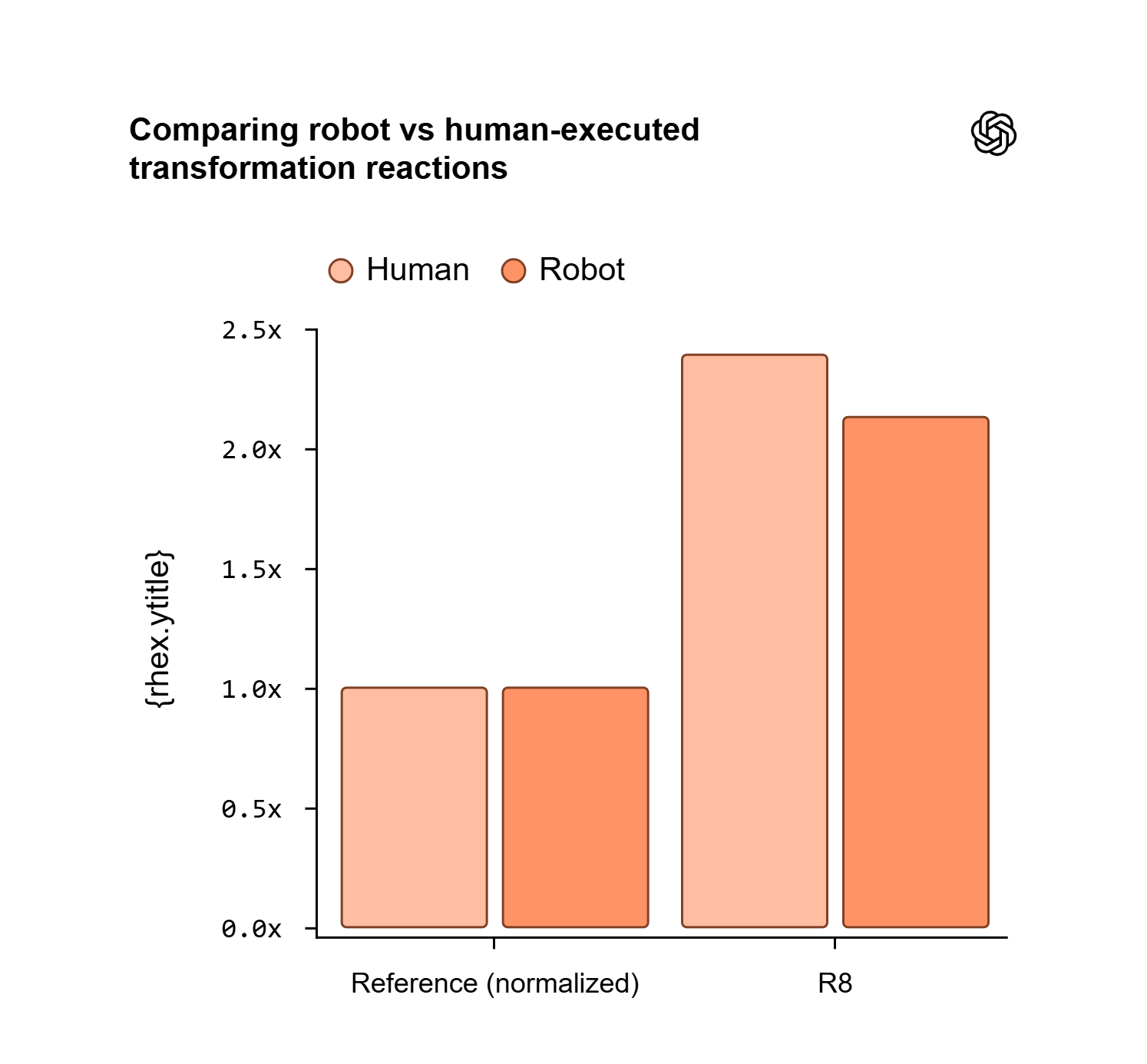
In this study, both human researchers and the autonomous robot executed an improved cloning protocol (R8) against a standard HiFi baseline. Human execution achieved a 2.39× improvement, while the robot achieved 2.13× or 89% of human performance, with consistent protocol ranking.
By enabling faster, repeatable robotic operations, the system demonstrated how intelligent automation can improve speed, consistency and scale in molecular biology workflows. This research offers a glimpse into how lab robots can work side-by-side with scientist to help accelerate research and breakthrough discovery. Read the complete paper here.
Excerpt from the OpenAI paper
Accelerating scientific progress is one of the most valuable ways AI can benefit humanity. With GPT‑5, we're beginning to see early signs of this—not only in helping researchers move faster through the scientific literature, but also in supporting new forms of scientific reasoning, such as surfacing unexpected connections, proposing proof strategies, or suggesting plausible mechanisms that experts can evaluate and test.
Progress to date has been most visible in fields like mathematics, theoretical physics, and theoretical computer science, where ideas can be rigorously checked without physical experiments. Biology is different: most advances depend on experimental execution, iteration, and empirical validation in the laboratory.
To help understand how frontier models behave in these settings, we worked with Red Queen Bio, a biosecurity start-up, to build an evaluation framework that tests how a model proposes, analyzes, and iterates on ideas in the wet lab. We set up a simple molecular biology experimental system and had GPT‑5 optimize a molecular cloning protocol for efficiency.
Over multiple rounds of experimentation, GPT‑5 introduced a novel mechanism that improved cloning efficiency by 79x. Cloning is a fundamental molecular biology tool. The efficiency of cloning methods is critical for creating large, complex libraries central to protein engineering, genetic screens, and organismal strain engineering. This project offers a glimpse of how AI could work side-by-side with biologists to speed up research. Improving experimental methods will help human researchers move faster, reduce costs, and translate discoveries into real-world impact.
Robotic system
To increase the throughput of this model experimental system, Robot on Rails and Red Queen Bio collaborated to build a robotic system that takes in a natural language cloning protocol and executes it in the wet lab.
The system combines three components: 1) a human-to-robot LLM that converts plain English into the robot's actions; 2) a vision system that identifies and localizes labware in real time; and 3) a robotic path planner that determines how to carry out each action safely and accurately. The result is a flexible, generalized lab robot that was further optimized for variants of the Gibson cloning protocol.
We tested whether the autonomous robot could execute a complete cloning experiment by running two protocols simultaneously: the standard HiFi method and R8, the top-performing AI-modified protocol from the first optimization round.
We compared the robot's work to human-performed experiments at each step. The robot successfully handled the transformation process, which required diverse physical operations: transferring and mixing liquids, moving sample tubes, applying controlled heat to cells, and spreading cells onto growth plates. When compared directly with human-performed transformations, the robot generated similar quality data with equivalent improvements over baseline, showing early potential for automating and accelerating biological experiment optimization.
While the fold-changes between the robot and human experiments were similar, absolute colony counts from the robot were approximately ten-fold lower than manual execution, indicating areas for improvement such as liquid handling precision, temperature control calibration, and replicating the nuances of manual cell handling techniques.
Both the standard HiFi method (baseline) and the improved R8 method were executed by human researchers and the autonomous robot, with transformation efficiencies normalized to respective HiFi baseline controls (set to 1.0). Human-executed R8 showed 2.39-fold improvement; robot-executed R8 achieved 2.13-fold improvement (89% of human performance), demonstrating comparable protocol ranking despite lower absolute yields.
The future (according to OpenAI)
We believe that these experiments offer a snapshot of what future AI-accelerated science will look like: models continually learning and interacting with the real world. Although our experiments excluded human intervention to purely measure model capabilities, we're particularly excited about AI helping human scientists design experiments and contribute to research breakthroughs.
As we work to accelerate scientific progress safely and responsibly, we also seek to evaluate and reduce risks, particularly those related to biosecurity. These evaluations results show that models can reason in the wet lab to improve protocols, and may have implications for biosecurity as highlighted in OpenAI's Preparedness Framework. We are committed to building necessary and nuanced safeguards at a model and system level to reduce these risks, as well as develop evaluations to track current levels.